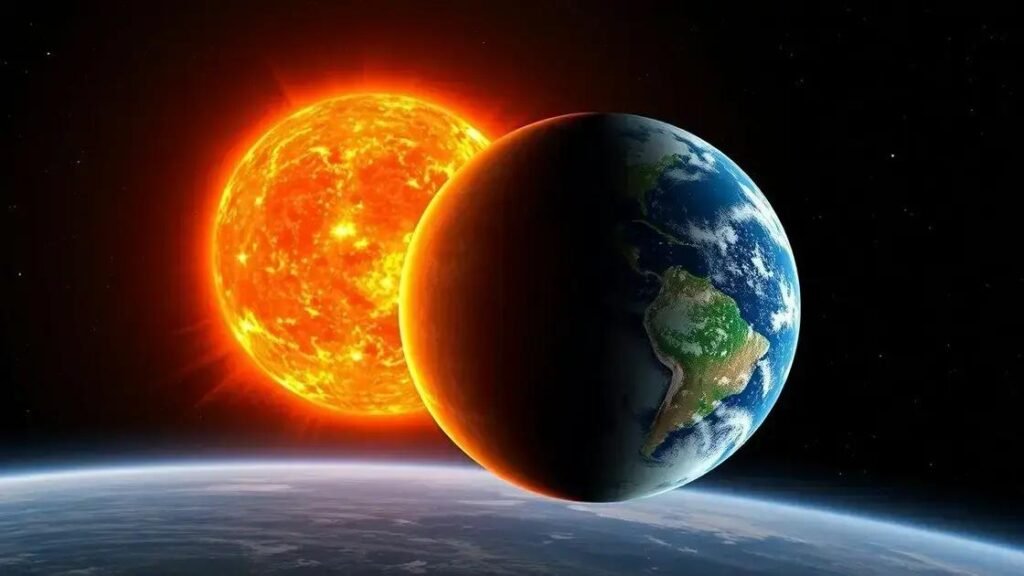
Earths in the Sun measures the vast size difference, with about 1.3 million Earths able to fit inside the Sun’s enormous volume due to its massive diameter and gaseous composition.
Have you ever wondered just how many Earths in the Sun could actually fit inside our giant star? The scale difference is mind-blowing and helps us see our place in the universe a little clearer.
understanding the size of the sun
The Sun is a massive star at the center of our solar system. Its size is truly enormous compared to Earth and other planets. The Sun’s diameter is about 1.39 million kilometers, which is roughly 109 times the diameter of Earth. This tremendous size means the Sun has a huge volume and mass, making it the dominant gravitational force in our solar system.
Understanding the size of the Sun helps us appreciate how small Earth really is. Even though the Sun is mainly made of gases like hydrogen and helium, its volume is so vast that it can hold approximately 1.3 million Earths inside. This comparison gives us a clear idea of the scale of celestial bodies and the forces at play.
Measuring the Sun
Scientists measure the Sun’s size using advanced telescopes and spacecraft. Observations from Earth and space missions allow precise calculations of its diameter and surface features. These measurements are crucial to understanding how the Sun works, including its energy output and impact on the solar system.
The Sun’s massive size also plays a major role in its life cycle, affecting everything from solar flares to its eventual transformation into a red giant. By grasping its size, we better understand the dynamics of our star and how it influences our planet and life on Earth.
comparison between the sun and the earth
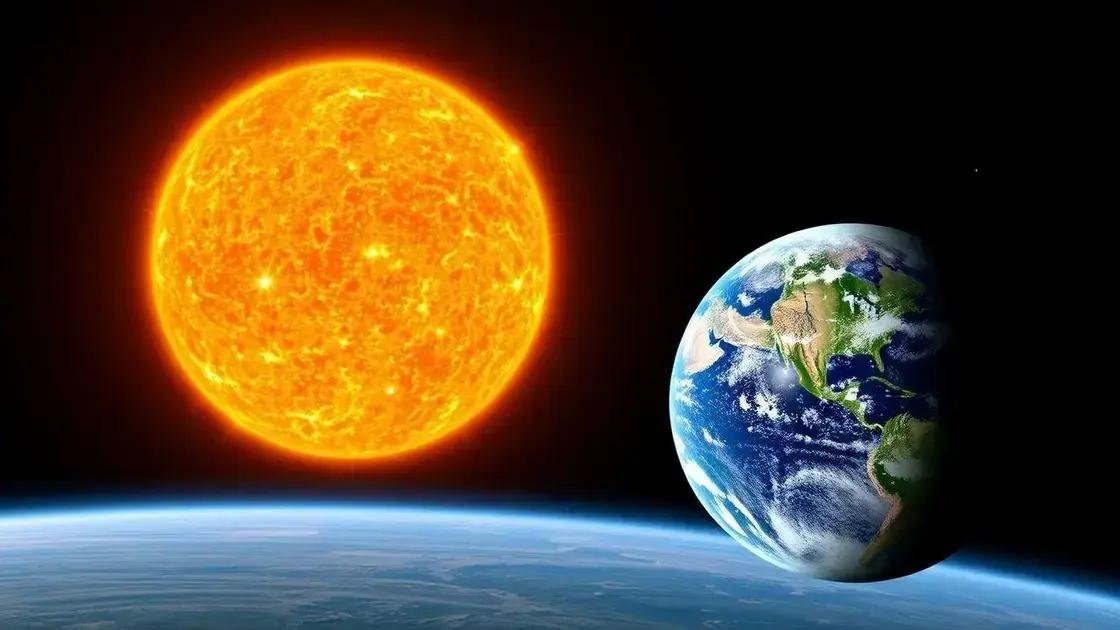
The comparison between the Sun and the Earth reveals a striking difference in size and structure. The Sun is a gigantic ball of hot plasma, while Earth is a solid, rocky planet. The diameter of the Sun is about 109 times larger than Earth’s diameter, making it easy to see how much larger the star is.
In terms of volume, the Sun can hold over 1.3 million Earths inside it. This shows just how immense the Sun is compared to our planet. The Sun’s mass is also overwhelmingly greater, containing about 99.86% of the total mass of the entire solar system.
Structural Differences
The Earth is made mostly of rock and metal, with a solid surface we can stand on. The Sun, on the other hand, is composed mostly of hydrogen and helium gases in a plasma state. It has layers, such as the core where nuclear fusion occurs, the radiative and convective zones, and the outer atmosphere called the corona.
Understanding the size and composition differences helps explain why the Sun produces enormous amounts of energy through fusion while Earth supports life with a solid environment and atmosphere. This fundamental comparison deepens our knowledge about the unique roles these two bodies play in the solar system.
volume calculation of the sun and earth
Calculating the volume of the Sun and Earth helps us understand the massive difference in their sizes. Volume measures how much space an object occupies, and it is calculated differently depending on the shape of the object. Both the Sun and Earth are close to spherical, so we use the formula for the volume of a sphere: V = \frac{4}{3} \pi r^3, where r is the radius.
The Earth’s average radius is about 6,371 kilometers. Using the formula, Earth’s volume is roughly 1.08 billion cubic kilometers. This is the space our planet occupies in the vast solar system.
In contrast, the Sun’s average radius is about 696,340 kilometers. Applying the same formula, the Sun’s volume is approximately 1.41 trillion cubic kilometers. This means the Sun is over 1,000 times larger in volume than Earth.
Visualizing the volume difference
To put it simply, you could fit around 1.3 million Earths inside the Sun if it were hollow. This volume comparison highlights how much bigger the Sun is. It also explains why the Sun’s gravitational pull dominates the entire solar system.
Understanding these calculations helps scientists learn more about the structure and behavior of celestial bodies. It also allows us to appreciate the amazing scale of our universe and the unique place Earth holds within it.
how many earths fit inside the sun
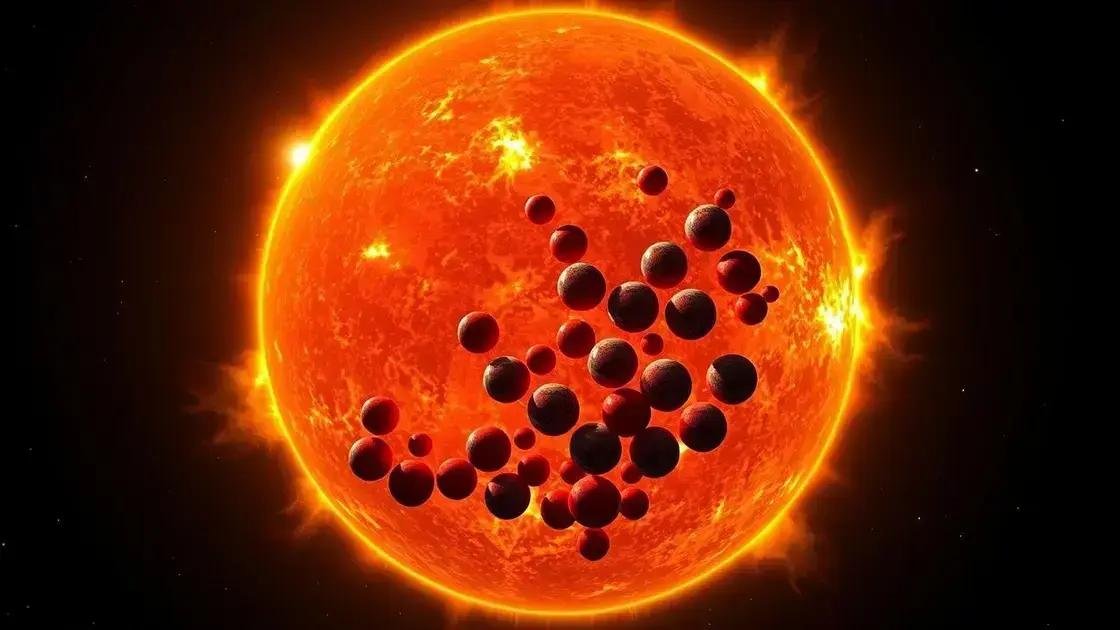
The question, how many Earths fit inside the Sun, helps us grasp the vast difference in size between our planet and the star at the center of our solar system. Given the enormous volume of the Sun compared to Earth, the answer is staggering.
Using volume calculations, scientists estimate that about 1.3 million Earths could fit inside the Sun. This number illustrates just how immense the Sun is. Imagine fitting all the Earths inside a hollow space shaped like the Sun—that’s the scale we’re dealing with.
What this means for our solar system
The Sun’s huge size makes it the main source of energy and gravity for everything orbiting around it. Although Earth is much smaller, it plays a crucial role in supporting life thanks to its atmosphere, water, and position in the solar system.
Understanding how many Earths can fit inside the Sun not only highlights the immense power and scale of the Sun but also helps us appreciate Earth’s unique qualities in contrast.
why size matters in astronomy
Size plays a crucial role in astronomy because it helps us understand the physical properties and behavior of celestial objects. Larger objects like stars have stronger gravitational pulls, which affect nearby planets and other bodies. For example, the Sun’s massive size allows it to hold the solar system together through its gravity.
Understanding size also helps explain phenomena such as light emission, lifespan, and formation. A star’s size influences how much energy it produces and how long it will last. Smaller stars burn fuel slowly and live longer, while massive stars use up fuel quickly and have shorter lifespans.
Size and telescopic observation
Knowing the size of planets, stars, and galaxies also helps astronomers choose the right instruments for observation and measurement. It helps predict how objects will move and interact in space, making size a key factor in studying the universe’s dynamics.
Finally, size comparisons allow us to visualize and appreciate our place in the cosmos. Seeing how tiny Earth is compared to the Sun or other stars gives perspective on space and helps in teaching and exploration.
visualizing the sun’s scale with earth models
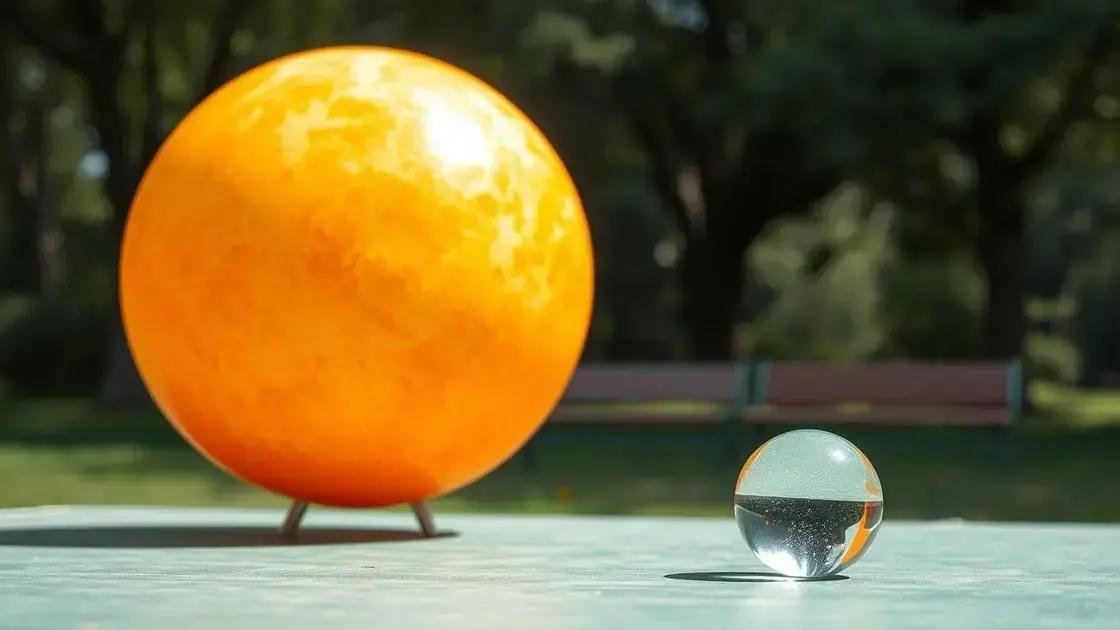

Visualizing the Sun’s scale with Earth models helps make the massive size difference easier to understand. One common method is to use scaled-down models where Earth’s size is compared directly to the Sun’s size using miniatures or graphics.
For example, if the Sun were a large beach ball about 1 meter in diameter, Earth would be a tiny marble just 9 millimeters wide placed several meters away. This visual aid shows clearly how small Earth is next to the Sun.
Educational models and tools
Many educational tools use these scaled models to teach students and adults about space. These include globe sets, 3D printed models, and virtual reality experiences that accurately reflect the size ratio between Earth and the Sun.
Such models help bridge the gap between abstract numbers and real-world perception. They give a hands-on, visual understanding of size differences that are otherwise hard to imagine given the huge scales involved.
Using models also supports learning about orbits, distances, and the solar system’s vastness while making astronomy more accessible and engaging.
historical perspective on measuring celestial sizes
Measuring the sizes of celestial bodies has been a challenge throughout history. Early astronomers used simple tools and observations from Earth to estimate sizes and distances. For example, ancient Greeks observed lunar eclipses to understand the Moon’s size relative to Earth.
One of the earliest breakthroughs came from Aristarchus of Samos, who used geometry to estimate the relative distances and sizes of the Sun and Moon around 270 BC. His work laid the groundwork for later, more precise measurements.
Advances with telescopes
The invention of the telescope in the 17th century revolutionized astronomy. Scientists like Galileo Galilei observed sunspots and planetary transits, which gave more accurate data about the Sun and planets’ sizes.
Later, astronomers used parallax methods and spacecraft measurements to gain precise size and distance information. These advancements helped us understand the vast scales of our solar system and beyond.
The ability to measure celestial sizes accurately is key to learning about the structure and evolution of stars, planets, and galaxies. It also influences navigation, space missions, and our understanding of the universe.
the sun’s composition and its effect on size
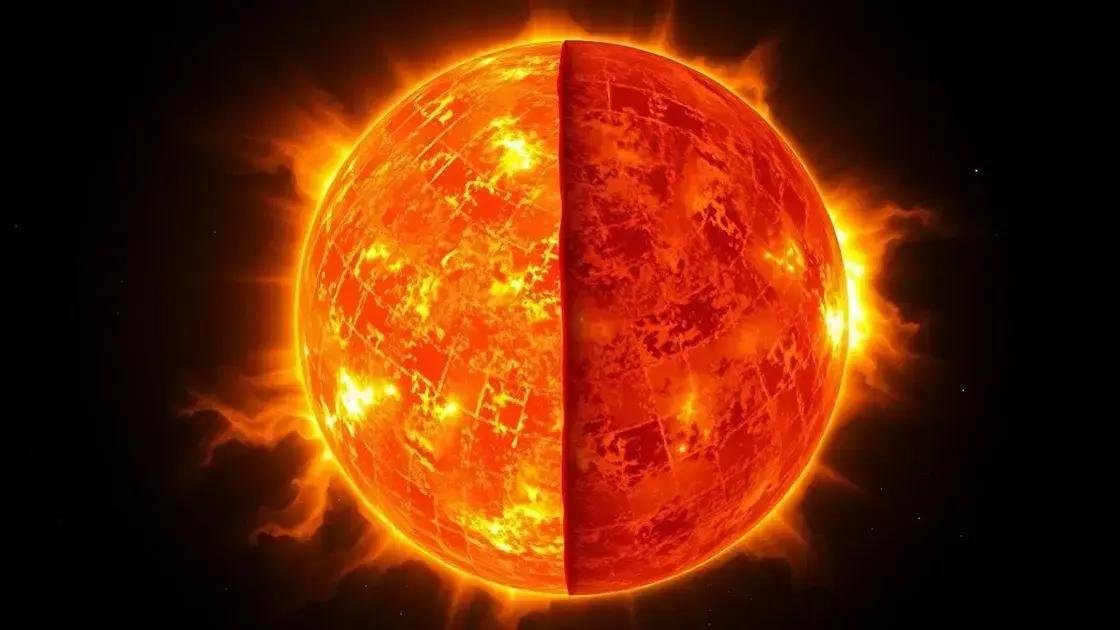
The Sun’s composition mainly includes hydrogen and helium, which makes it a massive ball of hot plasma rather than a solid object. About 74% of the Sun’s mass is hydrogen, and roughly 24% is helium, with smaller amounts of heavier elements. This gaseous makeup contributes to the Sun’s huge size because gases expand more than solids.
The Sun’s size is not fixed; it is constantly changing due to nuclear fusion reactions happening in its core. These reactions convert hydrogen into helium, releasing tremendous energy that causes the Sun to shine and maintain its volume against gravitational collapse.
Layers and structure effects
The Sun consists of layers such as the core, radiative zone, convective zone, and the outer atmosphere called the corona. Each layer plays a role in energy transfer and affects the Sun’s overall size and shape. The outer layers are less dense but cover a large volume, making the Sun appear much larger.
The Sun’s composition also affects its brightness and temperature. Because it is mostly hydrogen, it can sustain fusion for billions of years, creating enough pressure to keep the Sun’s size stable while slowly changing over time.
what earth’s size means for life
Earth’s size plays a vital role in supporting life as we know it. The planet’s diameter and gravity are just right to hold an atmosphere capable of sustaining water in liquid form, which is essential for life. If Earth were significantly larger or smaller, maintaining this delicate balance would be difficult.
The right size also allows Earth to have a stable climate and magnetic field. The magnetic field protects us from harmful solar radiation, while Earth’s size and rotation influence weather patterns and seasons.
Impact on biodiversity and ecosystems
Because of its size, Earth has varied environments like mountains, oceans, and forests that support a wide range of plants and animals. This diversity is crucial for ecosystems that provide food, oxygen, and other resources needed for life.
Earth’s size also affects its geological activity, such as plate tectonics, which recycles nutrients and maintains the planet’s habitability over millions of years.
the vastness of the solar system

The solar system is incredibly vast, stretching billions of kilometers from the Sun to the outermost dwarf planets and beyond. The distances between planets are so large that light, traveling at nearly 300,000 kilometers per second, takes minutes or even hours to cross these gaps.
Understanding the vastness helps us appreciate how small Earth really is within this immense space. For example, the distance from Earth to the Sun is about 150 million kilometers, called an astronomical unit (AU), but Neptune, the farthest major planet, is about 30 AU away.
Beyond the planets
The solar system also contains the asteroid belt, Kuiper Belt, and the distant Oort Cloud, which hold countless small objects. These regions extend the system far beyond the planets, highlighting the enormous space influenced by the Sun’s gravity.
The vastness makes space exploration challenging, as spacecraft take years to travel even to our closest neighbors. It also reminds us of the incredible scale and complexity of the cosmic neighborhood we live in.
other planets compared to earth and the sun
When comparing other planets to Earth and the Sun, the size differences are quite remarkable. Planets in our solar system vary widely in size, composition, and distance from the Sun.
Gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn are much larger than Earth but still tiny compared to the Sun. Jupiter, the largest planet, has a diameter about 11 times that of Earth, but the Sun is about 10 times larger than Jupiter.
Rocky planets versus gas giants
Earth, Mars, Venus, and Mercury are terrestrial planets with solid surfaces. Among these, Earth is third in size, larger than Mars and Mercury but smaller than Venus. These rocky planets are far smaller than the gas giants, which have thick atmospheres and no solid surface.
The size comparisons help us understand each planet’s gravity, atmosphere, and potential to support life. For example, Earth’s moderate size allows it to hold an atmosphere suitable for life, whereas larger gas giants cannot support life as we know it.
Knowing these size relationships also aids in learning about planetary formation and the dynamic nature of our solar system.
how scientists measure space objects

Scientists measure space objects using a variety of methods depending on the distance and size of the object. One common technique is parallax, which measures the apparent shift of an object against distant stars as Earth orbits the Sun. This helps calculate distances to nearby stars.
For closer objects like planets and moons, radar and laser ranging are used. Scientists send signals towards the object and measure the time it takes to bounce back, giving accurate distance measurements.
Telescope observations
Telescopes equipped with advanced technology allow researchers to observe the size, shape, and movement of space objects. Spectroscopy analyzes the light from stars and planets to determine composition and relative velocity.
Spacecraft missions provide the most precise measurements by approaching or orbiting objects directly, using onboard instruments to capture detailed data on size, mass, and surface characteristics.
Combining these methods enables scientists to build accurate models of objects in space, improving our understanding of the universe’s vast and complex nature.
fun facts about the sun and earth size
Here are some fun facts about the Sun and Earth’s size that highlight their fascinating differences and similarities.
The Sun is so large that about 1.3 million Earths could fit inside it, showing just how massive the star really is. Despite this, Earth plays an important role in supporting life thanks to its unique size and conditions.
Interesting size facts
Earth is the fifth largest planet in the solar system, but it is the largest of the terrestrial planets. Its diameter is about 12,742 kilometers, while the Sun’s diameter is roughly 109 times greater.
The Sun’s volume changes slightly over time due to solar activity, but overall it remains stable for billions of years. Earth’s size, on the other hand, allows it to maintain a strong magnetic field, which protects life from harmful solar radiation.
Although the Sun dominates in size and mass, a day on Earth is just 24 hours, whereas the Sun takes about 25 days to complete one rotation at its equator due to its gaseous nature.
implications of size differences in space exploration

The significant size differences between planets, moons, and stars have major implications for space exploration. Larger bodies like the Sun emit vast amounts of energy and radiation, which spacecraft and astronauts must be protected from to ensure mission safety.
Smaller bodies like Earth have the right conditions for human life but pose challenges such as gravity that requires spacecraft to have enough power for launch and landing. Size and gravity affect fuel needs, travel time, and mission design.
Exploring massive versus small objects
When exploring massive objects like gas giants, probes must withstand strong magnetic fields and intense radiation. For smaller moons or asteroids, landing and navigation require precise control because of low gravity and irregular shapes.
Size differences also guide choices about suitable spacecraft types and exploration methods, from orbiters and landers to rovers and sample-return missions. Understanding these size-related challenges helps agencies plan safer and more efficient space exploration projects.
Understanding the size difference between Earth and the Sun
The vast size difference between Earth and the Sun highlights the incredible scale of our solar system. Knowing that about 1.3 million Earths could fit inside the Sun helps us appreciate both the power of the Sun and the uniqueness of our planet.
These size differences affect many aspects of space science and exploration, from energy and gravity to spacecraft design and mission challenges. By studying and visualizing these differences, we can better understand our place in the universe and continue to explore the wonders beyond.
Exploring size in astronomy not only expands our knowledge but also inspires curiosity about the vast universe we live in.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Earth and the Sun Size
How many Earths can fit inside the Sun?
Approximately 1.3 million Earths can fit inside the Sun based on their volume comparison.
Why is the Sun so much larger than Earth?
The Sun is a massive ball of hot plasma composed mainly of hydrogen and helium, giving it a huge volume compared to the solid Earth.
How does the size difference affect space exploration?
The size difference impacts mission design, fuel requirements, and spacecraft protection due to varying gravity, radiation, and atmospheric conditions.
What methods do scientists use to measure the size of the Sun and Earth?
Scientists use techniques like telescopic observations, parallax measurements, radar ranging, and spacecraft data to measure sizes accurately.
Why is Earth’s size important for supporting life?
Earth’s size allows it to hold a stable atmosphere, maintain a magnetic field, and support diverse ecosystems necessary for life.
How can visual models help us understand the scale of the Sun and Earth?
Scaled models, such as comparing the Sun to a beach ball and Earth to a marble, help people grasp the vast size difference in a tangible way.






