About 1.3 million Earths can fit inside the Sun, highlighting the vast difference in size and volume between our small planet and the massive star that powers the solar system.
Have you ever wondered just how many Earths in the Sun could fit? It’s a mind-boggling concept that helps us grasp the vast scale of our star compared to our tiny planet. Let’s dive into these cosmic proportions together.
understanding the size difference between the sun and the earth
The sun is incredibly larger than the Earth, both in size and volume. To understand this difference, we look at the diameters: the sun’s diameter is about 1.39 million kilometers, while Earth’s is only about 12,742 kilometers. This means the sun is roughly 109 times wider than Earth.
Volume comparison
When comparing volume, the difference becomes even more astonishing. The sun could hold about 1.3 million Earths inside it! This is because volume increases with the cube of the diameter, so a much larger diameter causes an enormous increase in volume.
Why the size difference matters
The massive scale of the sun compared to Earth impacts everything from gravity to the energy the sun emits. Our planet is just a tiny speck next to this glowing giant, which fuels life and controls the entire solar system.
Understanding these size differences helps us grasp our place in the universe and appreciate the vastness beyond our world.
volume comparison: how much space does the sun occupy
The sun’s volume is vast, far beyond what we experience with objects on Earth. It occupies about 1.41 x 1018 cubic kilometers of space. To put it simply, volume is the amount of three-dimensional space an object takes up.
How does it compare to Earth?
Earth’s volume is approximately 1.08 x 1012 cubic kilometers. This means the sun’s volume is about 1.3 million times greater than that of Earth. Imagine trying to fit 1.3 million Earths inside a giant bubble—that’s the sun!
Understanding volume and space
Volume depends on the shape and size of an object. Since the sun is a nearly perfect sphere, its volume is calculated using the formula for a sphere: (4/3)πr³, where r is the radius. This huge volume accounts for the vast space the sun occupies in our solar system.
This enormous capacity influences not only gravity but also the sun’s ability to produce energy through nuclear fusion at its core, sustaining life on Earth.
visualizing earths inside the sun with simple analogies
To better grasp how many Earths can fit inside the sun, simple analogies help. Imagine the sun as a large beach ball. If Earth were a small marble, about 1 centimeter wide, you could fit about 1.3 million marbles inside that big beach ball.
Using common objects for scale
Another way to visualize this is thinking of a basketball and a pea. The basketball represents the sun, and the pea represents Earth. Imagine filling the basketball with millions of tiny peas—that’s the scale difference between the two.
The power of analogy
Analogies make huge numbers easier to understand. Instead of just hearing ‘1.3 million Earths,’ picturing familiar sizes shows the massive scale of the sun’s volume and helps make this huge number more relatable.
These comparisons also highlight the vast space the sun occupies in our solar system and why it’s so central to life on Earth.
why size matters: the sun’s role in the solar system

The sun’s enormous size is crucial to its role in the solar system. Because it holds more than 99% of the solar system’s mass, its gravity keeps all the planets, including Earth, in orbit. This gravitational pull is what makes the solar system stable.
Energy and life
The sun’s size also allows it to produce vast amounts of energy through nuclear fusion at its core. This energy travels to Earth as light and heat, making life possible and driving our planet’s climate and weather.
Impact on planetary orbits
The sun’s large mass controls how planets move, their speed, and their distance from the sun. If the sun were smaller, or less massive, the planets’ orbits would change, likely making life on Earth impossible.
Its size is also why the sun can influence other phenomena like solar flares, which can affect technology and communication on Earth.
how scientists measure the size of celestial bodies
Scientists use various methods to measure the size of celestial bodies like the sun and Earth. One common technique is telescopic observation, which measures angles and distances with great accuracy.
Using parallax and radar
Parallax involves observing a planet from two different points in Earth’s orbit and calculating its distance by measuring the angle shift. Radar signals can also bounce off planets and return, giving precise distance measurements.
Calculating diameter and volume
Once distance is known, scientists measure the apparent size of the celestial body. They use formulas to translate this apparent size into actual diameter. Measuring the diameter allows them to calculate volume using the formula for a sphere.
These techniques are combined with space missions and satellites that provide direct measurements to improve accuracy. Understanding size helps scientists learn about composition, gravity, and behavior of these bodies in space.
the sun’s diameter versus earth’s diameter

The sun’s diameter is about 1.39 million kilometers, which makes it roughly 109 times larger than Earth’s diameter of about 12,742 kilometers. This vast difference highlights how small Earth is in comparison to our star.
Diameter explained
Diameter is the distance straight across a circle through its center. Since both the sun and Earth are nearly spherical, their diameter gives us a clear measure of their size.
Visualizing the difference
If Earth were the size of a basketball, the sun would be a gigantic sphere about the size of a small house. This striking comparison illustrates the sun’s massive scale and why it holds so much influence in our solar system.
Understanding this size difference helps us realize the sun’s powerful impact on Earth’s climate, gravity, and overall existence.
exploring layers of the sun and their sizes
The sun is made up of several distinct layers, each varying in size and function. Starting from the innermost part, the core is where nuclear fusion happens, producing the sun’s energy. The core spans about 20-25% of the sun’s total radius.
The radiative zone
Surrounding the core is the radiative zone, which extends to about 70% of the sun’s radius. Here, energy slowly moves outward through radiation, taking thousands of years to pass through.
The convective zone
The outer layer is called the convective zone. This is where energy moves more quickly through convection — hot plasma rises, cools, and sinks. This zone reaches the sun’s surface, which we see as the photosphere.
Above the photosphere, the sun’s atmosphere includes the chromosphere and the corona, which can only be seen during a solar eclipse. Each layer plays a vital role in how the sun produces energy and affects space weather that impacts Earth.
comparison of earth to other planets in the solar system
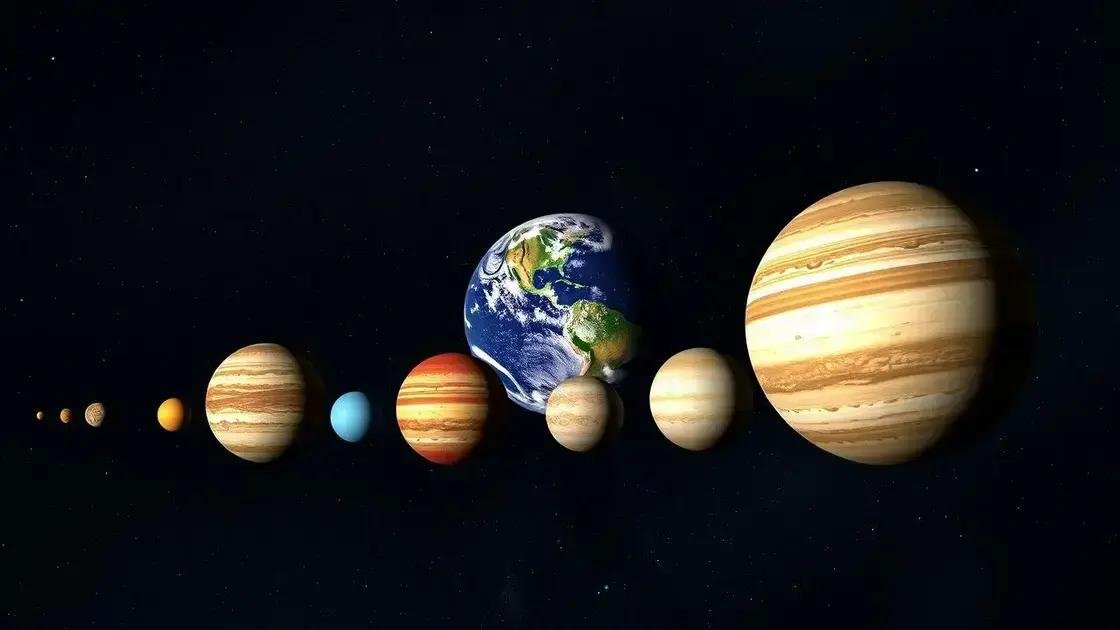

Earth is just one of eight planets orbiting the sun, and its size compares interestingly to the others. Among the rocky planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, Earth is the largest, with a diameter of about 12,742 kilometers.
Comparing Earth to gas giants
The gas giants—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—are much bigger. Jupiter, the largest planet, has a diameter over 11 times that of Earth. Saturn follows, then Uranus and Neptune, all dwarfing Earth in size.
Why size differences matter
These size variations affect each planet’s gravity, atmosphere, and potential to host life. Earth sits in the “Goldilocks zone,” with a size and distance from the sun that supports liquid water and life as we know it.
Understanding Earth’s size in relation to other planets helps us appreciate not just our planet’s uniqueness, but also the diversity of the solar system.
the sun’s mass and its relation to volume
The sun’s mass is about 1.989 x 1030 kilograms, which is roughly 330,000 times the mass of Earth. While its volume is huge, its mass is concentrated tightly due to its dense core made mostly of hydrogen and helium.
Mass versus volume
Volume measures how much space an object occupies, while mass measures how much matter it contains. The sun’s huge volume holds vast amounts of hydrogen and helium gases, but the core’s density packs in most of the sun’s mass.
Why mass matters
The sun’s mass creates a strong gravitational pull that holds planets in orbit and drives nuclear fusion reactions at the core. These reactions produce the energy that powers the sun and makes life on Earth possible.
Understanding the relationship between the sun’s mass and volume helps reveal how its physical properties affect its power and place in the solar system.
how the sun’s size affects its gravity and light

The sun’s massive size directly impacts its gravity and the amount of light it emits. Because the sun contains over 99% of the solar system’s total mass, its gravitational pull is strong enough to keep all planets, asteroids, and comets in stable orbits.
Gravity and orbit stability
The huge gravity comes from the sun’s dense core where nuclear fusion occurs. This gravity pulls the planets toward the sun, balancing the outward motion of planets and creating stable orbits.
Light and energy production
The sun’s size allows it to hold a large core where hydrogen atoms fuse into helium, generating massive amounts of energy. This energy travels outward as light and heat, reaching Earth as sunlight that supports all life.
Because of its scale, the sun shines with immense brightness and provides the energy needed for ecosystems, weather patterns, and climate on Earth. Its size and gravity work together to make the solar system function smoothly.
historical perspectives on measuring the sun
Throughout history, humans have been fascinated by the sun and its size. Early civilizations estimated the sun’s size and distance using simple tools like sticks and shadows. For example, the ancient Greek scientist Aristarchus used geometry and observations of lunar eclipses to estimate the sun’s distance from Earth.
Advances during the Renaissance
During the Renaissance, more precise measurements were made thanks to improved telescopes and mathematical techniques. Scientists like Galileo and Kepler contributed to our understanding of the solar system, helping measure the sun’s size with greater accuracy.
Modern methods
Today, scientists use radar, satellites, and space probes to measure the sun with incredible precision. These tools have helped refine estimates of the sun’s diameter, mass, and distance, far beyond what early astronomers imagined.
Historical efforts laid the foundation for modern astronomy and continue to inspire curiosity about the vastness of space.
fun facts about the sun’s size and earth’s scale

The sun is so large that about 1.3 million Earths could fit inside it. This massive size helps explain the sun’s powerful influence on our solar system.
Quick facts
Did you know that the sun’s diameter is about 109 times that of Earth? If Earth were the size of a nickel, the sun would be about as wide as a front door!
Interesting comparisons
The sun is 330,000 times as massive as Earth, but since it’s made mostly of gas, it’s much less dense. Its huge volume combined with lower density explains these surprising properties.
These fun facts help us better understand the vast difference in scale between our planet and its central star.
how the earth would look if placed inside the sun
If you placed Earth inside the sun, it would be like a tiny marble dropped into a huge fiery ball. The sun’s volume is so large it could hold about 1.3 million Earths inside it.
The scale difference
Earth would be just a small dot, barely visible, compared to the sun’s vast, glowing surface. The intense heat and pressure inside the sun would quickly destroy Earth as we know it.
Imagining the size visually
If the sun were a large sphere you could stand next to, Earth would be a tiny pebble in your hand. This comparison helps emphasize the extreme size difference and power of our star.
Visualizing Earth inside the sun reveals just how massive and dominant the sun is in our solar system.
impacts of the sun’s sheer size on earth’s climate

The sun’s enormous size plays a crucial role in shaping Earth’s climate. Its massive energy output provides the heat and light necessary to sustain weather patterns and support life on our planet.
Energy distribution
The sun radiates energy evenly, but Earth’s tilt and orbit cause variations in sunlight, leading to seasons and climate zones. Without the sun’s powerful energy from its vast size, these patterns wouldn’t exist.
Influence on global temperatures
Changes in the sun’s activity, like solar flares or sunspots, can slightly affect Earth’s temperature. Although these variations are small, they demonstrate the sun’s direct impact on our climate system.
The sun’s size ensures a steady flow of energy, helping maintain stable climates that allow ecosystems to thrive. Understanding this connection highlights how our star’s sheer scale influences life on Earth.
Understanding the Scale of the Sun and Earth
The vast difference between the sun and Earth reveals the incredible scale of our solar system. Knowing how many Earths fit inside the sun helps us appreciate the sun’s power and importance.
The sun’s size affects everything from gravity that holds planets in orbit to the energy that drives Earth’s climate and life. Learning about this relationship deepens our connection to the universe around us.
By exploring the sun’s size, layers, and influence, we gain better insight into our place in the cosmos and the delicate balance that supports life on Earth.
FAQ – Common Questions About Earth and the Sun Size Comparison
How many Earths can fit inside the Sun?
About 1.3 million Earths can fit inside the Sun based on volume comparison.
Why is the Sun so much bigger than Earth?
The Sun is a massive star made mostly of hydrogen and helium, which makes it much larger than Earth, which is a rocky planet.
How does the Sun’s size affect Earth’s climate?
The Sun’s size allows it to emit vast energy that drives Earth’s weather patterns, climate, and supports life.
What is the difference between the Sun’s mass and volume?
Volume is the space the Sun occupies, while mass is the amount of matter. The Sun’s core has very high mass density compared to its volume.
How is the Sun’s size measured?
Scientists use telescopes, radar, satellites, and space missions to measure the Sun’s diameter and volume precisely.
What would happen if Earth were placed inside the Sun?
Earth would be a tiny speck inside the Sun, quickly destroyed by intense heat and pressure inside the Sun’s layers.






